Welcome to our blog, where we explore the fascinating realm of EPAT therapy. You’re in the perfect place whether you want to improve your physical performance or get relief from chronic pain. The technology known as Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology, or EPAT, uses sound waves to promote healing and regeneration. Come along as we discuss the science underlying EPAT, highlight patient success stories, and offer insights into how this innovative therapy can improve your quality of life.
Table of Contents
Together, let’s set out on this path to pain-free living.
What Is EPAT Therapy?
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology, or EPAT, is a non-invasive therapeutic approach used to treat a range of musculoskeletal therapy disorders and encourage tissue regeneration. This novel therapy stimulates the body’s healing mechanisms using sonic waves. High-energy acoustic pulses that deeply penetrate the tissue are applied to the afflicted area during an EPAT session. These pulses set off a series of biological reactions that include improved nutrient delivery, increased blood flow, and the release of growth factors that aid in tissue regeneration and repair.
It is well-recognized that EPAT therapy works well for treating chronic pain syndromes, tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, and muscle strains. With little recovery time and almost no chance of complications, EPAT provides patients with a non-surgical option for invasive or surgical procedures. Because of its capacity to hasten healing and reduce discomfort, EPAT has emerged as the go-to option for athletes, physically active people, and everyone else looking for treatment for musculoskeletal conditions.
Conditions Treated With EPAT Therapy
Plantar fasciitis is one of the main problems addressed with EPAT therapy; it is frequently the source of heel discomfort. EPAT encourages tissue regeneration and reduces pain by using acoustic waves to target the damaged location. This allows people to return to their regular activities with less difficulty.
Tendinitis is another common musculoskeletal problem that responds effectively to EPAT therapy. Tennis elbow, patellar tendinitis, and Achilles tendonitis can all be treated with EPAT, which reduces discomfort and inflammation while encouraging tendon healing and restoration.
Additionally, EPAT therapy has demonstrated promise in treating ligament injuries and muscular strains. EPAT expedites the healing process by boosting nutrition delivery and blood flow to the injured tissues, enabling athletes and active people to resume their exercise or sport sooner.
EPAT therapy is especially beneficial for chronic pain syndromes like fibromyalgia and myofascial pain syndrome. Targeting trigger points and encouraging the relaxation of tense muscles, the acoustic waves reduce pain and enhance quality of life in general.
Furthermore, bone-related disorders such as stress fractures and non-union fractures have been treated using EPAT therapy. By encouraging bone remodeling and improving blood flow to the injured area, EPAT can lessen the likelihood of problems and speed up the healing process.
EPAT Therapy Procedure
The process of implementing EPAT therapy, or extracorporeal pulse activation technology, usually starts with an initial consultation with a medical professional who has received EPAT administration training. In order to decide whether EPAT is the best course of treatment, the patient’s symptoms and medical history are examined during this session.
Depending on the area being treated, the patient is positioned comfortably to begin the EPAT session, either sitting or lying down. Next, conductive gel is applied to the affected area to help transmit acoustic waves.
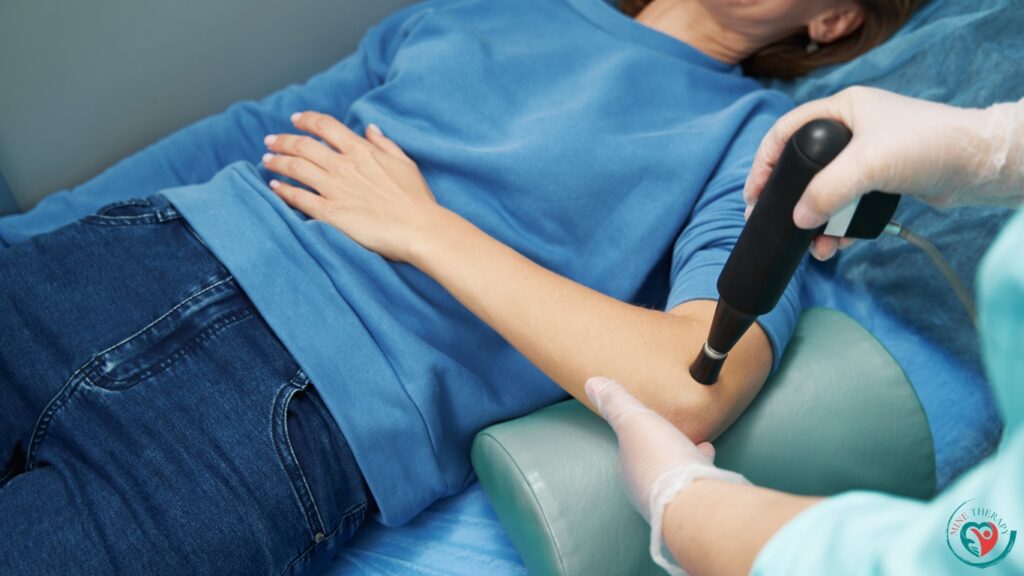
The healthcare provider next applies the EPAT device—which emits acoustic waves—to the targeted location. The apparatus penetrates deeply into the afflicted tissue by applying precise bursts of acoustic energy.
The acoustic wave intensity may be changed during the session depending on the patient’s comfort level and reaction to therapy. Depending on the size and location of the treatment area, the whole process usually takes 15 to 30 minutes.
After the EPAT session, patients may get back to their regular activities right away because the process involves little to no downtime. The treated area may cause some patients to feel slightly uncomfortable or sore, but this usually goes away in a few days.
Different Types Of EPAT Devices And Technologies
Devices that use EPAT (Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology) combine a number of technologies to treat musculoskeletal disorders and encourage the regeneration of new tissue. Here are a few examples of various kinds:
Electrohydraulic EPAT:
This kind of EPAT uses shock waves produced by an electrohydraulic projectile housed inside a handpiece. Shock waves are released when the bullet collides with a transmitter; these waves enter tissues and promote healing while reducing discomfort. It is frequently used to treat tendinopathies and plantar fasciitis.
Electromagnetic EPAT:
This gadget uses electromagnetic energy to cause controlled microtrauma to specific tissues, which sets off the body’s innate healing process. Due to its success in treating sports injuries and chronic pain, electromagnetic field electroacupuncture therapy (EPAT) is frequently preferred.
Radial Pressure Wave EPAT:
To increase blood flow and boost cellular metabolism, radial pressure wave devices produce acoustic waves that travel in a radial direction and penetrate tissues. Because of its versatility, this kind of EPAT can be used to treat a variety of musculoskeletal disorders, such as injuries to the muscles and tendons.
Piezoelectric EPAT:
These devices work with crystals that, when exposed to an electric field, produce sonic waves. As these waves move through tissues, they encourage cell renewal and repair. Piezoelectric electrophysiological therapy (EPAT) is prized for its accuracy and potency in focusing on specific damage sites.
Pneumatic EPAT:
Pneumatic EPAT devices use compressed air to create shock waves that treat injured tissues. They are frequently used to hasten recovery and reduce pain related to ailments, including tennis elbow and Achilles tendinopathy in orthopedic and sports medicine settings.
EPAT Therapy For Back Pain
For those with back discomfort, EPAT (Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology) therapy has become a potentially effective treatment alternative. Using acoustic waves, this non-invasive technique stimulates the body’s natural healing processes while focusing on the damaged area.
Depending on the location and intensity of the pain, the patient is usually pleasantly positioned while undergoing an EPAT session for back pain. This can involve sitting or lying down. Next, the medical professional applies a conductive gel to the skin to improve the transmission of acoustic waves.
Using the EPAT gadget, controlled bursts of acoustic energy are aimed at the particular region of the back that hurts. Profoundly penetrating the tissue, these waves stimulate enhanced blood flow, tissue regeneration, and the release of healing-promoting growth factors.
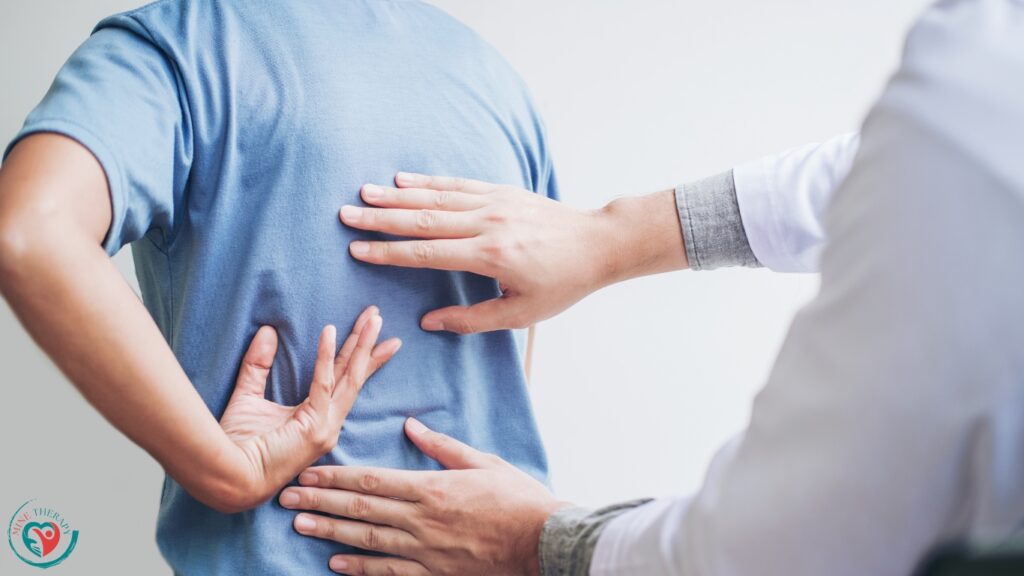
Back pain treated with EPAT therapy is frequently well tolerated, requiring little discomfort during the process. Patients may feel a little warm or tingly where the treatment is applied, but this usually goes away fast.
Depending on the severity of the back pain and each patient’s response to treatment, repeated EPAT sessions may be necessary to get the best benefits. EPAT therapy provides a secure and reliable non-surgical alternative for treating back pain, enabling patients to restore their mobility and enhance their quality of life without requiring intrusive procedures.
Does EPAT Therapy Help Mortons Neuroma?
Morton’s neuroma is an excruciating ailment marked by swelling of the tissue surrounding a nerve that leads to the toes. EPAT therapy has demonstrated the potential to relieve this condition. EPAT promotes tissue repair and increases blood flow to the affected area, which can help reduce related symptoms like pain and inflammation even though it doesn’t directly target the neuroma itself.
EPAT enhances the body’s natural healing processes by administering acoustic waves to the surrounding tissue, which may help lessen the discomfort brought on by Morton’s neuroma. Furthermore, EPAT therapy can assist in enhancing the affected foot’s function and mobility, enabling people to perform daily activities with reduced pain and suffering.
While EPAT therapy might not wholly remove Morton’s neuroma, it can be utilized in conjunction with other forms of treatment to manage symptoms and enhance general foot health. As with any medical problem, it’s imperative to speak with a healthcare professional to find the best course of action for specific needs.
Benefits Of EPAT Therapy
Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology, or EPAT, therapy provides a number of advantages for people looking for non-invasive treatments for a range of musculoskeletal disorders:
- Non-invasive: EPAT therapy is a safe and non-invasive substitute for conventional therapies because it doesn’t involve surgery or incisions.
- Minimal downtime: Following an EPAT session, patients can usually return to their regular activities right away because the process involves little to no downtime.
- Pain relief: EPAT therapy has been demonstrated to be an excellent means of reducing pain brought on by ailments like tendinitis, muscle strains, and plantar fasciitis, hence enhancing comfort and range of motion.
- Faster healing: EPAT therapy accelerates the healing of musculoskeletal injuries by promoting tissue regeneration and activating the body’s inherent healing processes. Increased range of motion and flexibility in the joints: EPAT therapy can help patients restore function and mobility in the afflicted areas.
- Versatility: EPAT therapy is a versatile treatment option for a variety of diseases. It can be used to treat a wide range of musculoskeletal problems, including tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, muscular strains, and chronic pain syndromes.
EPAT Therapy Side Effects
Although most people find EPAT (Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology) therapy to be safe and well-tolerated, a small number of people may have modest adverse effects. Usually transient, these adverse effects can include:
- Mild pain: During the EPAT session, some patients may feel a slight tingling feeling or discomfort, especially in the treated area. However, following the treatment, this soreness typically goes away quite fast.
- Redness or bruising: After an EPAT session, there may be a brief period when the treatment site becomes red or bruised. This is usually minor and goes away on its own in a few days.
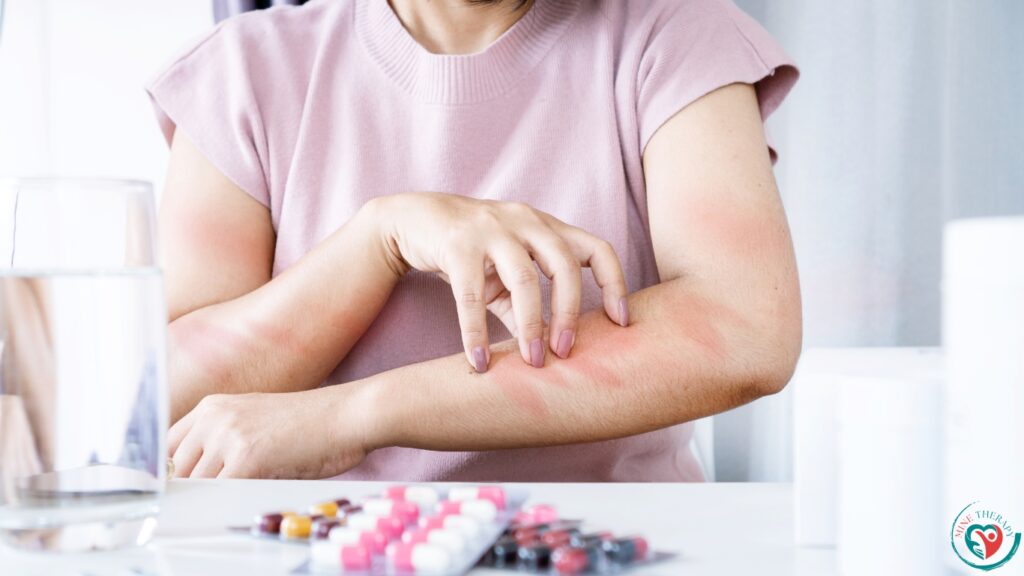
- Swelling: Immediately following EPAT therapy, a small amount of swelling may occasionally appear in the treated area. Still, this swelling usually goes down in a few hours or days.
- Rare complications: Although uncommon, more significant side effects like infection, numbness, or skin irritation are possible. To reduce the chance of problems, it’s critical to adhere to your healthcare provider’s post-treatment care instructions.
It is noteworthy that the majority of patients receiving EPAT therapy report little to no adverse effects. However, it’s crucial to speak with your healthcare practitioner right away if you have any questions or notice any strange symptoms following EPAT treatment.
Conclusion
To sum up, EPAT therapy (Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology) is a safe and efficient way to treat a variety of musculoskeletal issues. Through the use of acoustic waves, EPAT enhances mobility, lessens discomfort, and encourages tissue healing without requiring surgery or recovery time. For those looking for treatment for chronic pain and injury, EPAT has become a popular option because of its well-proven advantages and low adverse effects. Accept the life-changing potential of EPAT therapy and start your journey to a more pain-free, healthy living right now.
FAQs
Q: Does EPAT therapy cause pain?
A: Patients often handle EPAT therapy well, experiencing little discomfort during the process. Some people may feel a slight tingling or warming sensation in the treated area, although this normally goes away quickly.
Q: For results, how many EPAT sessions are necessary?
A: The severity of the disease and each patient’s responsiveness to treatment determine how many EPAT sessions are required. For best outcomes, however, patients usually go through a series of sessions spread out over a few weeks.
Q: Is EPAT treatment secure?
A: Indeed, when administered by a qualified healthcare professional, EPAT therapy is regarded as safe. The treatment is non-invasive and carries a low risk of consequences. To reduce any possible dangers, you must, however, adhere to your provider’s post-treatment care instructions.
Q: How soon after EPAT therapy can I get back to my regular activities?
A: With little to no recovery time following an EPAT session, patients may get back to their regular activities right away. To promote the best possible healing, it is advised to refrain from physically demanding activities or applying undue pressure to the treated area for a little while after treatment.
Q: Can one combine EPAT therapy with another form of treatment?
A: Indeed, to improve outcomes, EPAT therapy can be utilized in conjunction with other therapies, including physical therapy, stretching exercises, or orthotic devices, as part of a comprehensive treatment strategy. To enhance your recovery and increase results, your healthcare professional might design a treatment plan specifically for you and suggest a mix of therapies.

Trackbacks/Pingbacks